1315 issue: week ending 12 January 2024
Another Wasted Year Ahead
With MondAfrique
The island nation of Comoros on the Indian ocean is the first African nation to inaugurate the election season on the  African continent. And if the Comoros island is an example of what’s to come, Africa’s elections are going to count for nothing, with a few notable exceptions.
African continent. And if the Comoros island is an example of what’s to come, Africa’s elections are going to count for nothing, with a few notable exceptions.
In the Comoros, the incumbent President Azali Assoumani was declared on the 16 January 2024, the winner of rigged elections that triggered riots. As of January 18, Comoros witnessed a second day of turmoil resulting in one fatality and at least six injuries. Opposition parties contested the election results, alleging fraud and bias in favor of Assoumani, who, having changed the constitution in 2018 to bypass term limits, secured a fourth term with 62.97% of the vote. Accusations of dissent crackdown and protest bans were leveled against Assoumani, who also chairs the African Union.
President Assoumani and the Comoros are a template of what African politics looks like. African leaders have no interest in quitting their presidential seats without upheaval. Aside from some exceptions, there is no such thing as smooth presidential transition. Assoumani of the Comores has been in power since 1999.
So 2024 should be a record election year for Africa. Twenty countries, accounting for 346 million voters will be called to participate to elections that will mostly be rigged and decided in advance.
However, for those of you who live un western nations and where elections are the backbone of governance, it is worth noting that Africa has long been looking to distance itself from western-style democracy. Our colleagues from MondAfrique noted, rightly so, the for the most part, the forthcoming African elections have no democratic content and standards in them, citing the fact that different factors and actors have a more direct impact on the political systems in those countries. Among the factors cited by MondAfrique is the predominant role of the military in several countries like Mali, Niger and Guinea, the strength of traditional tribal structures, the rise of Islamic values favoring tradition over the law or finally the positive image of Vladimir Putin among many of African heads of state, factors that naturally clash with Western democratic values.
So of course, Africa does not have to mimic the west. It can create its own political model. But should we be pleased that a handful of ruthless rulers and their backers will win elections in advance? Not at all. Here is a snapshot of what to expect this year as African experience another election cycle.
Mauritania: Sudden customs tax increase at border with Morocco jolts food markets in Mauritania
This article is free, but it requires registration. Click on article to register or login
Mauritania: Christian group released from detention, expelled from Mauritania
This article is free, but it requires registration. Click on article to register or login
Sahel: Mali acquires lethal drones from Turkey
On January 4, 2024, the Malian military acquired six Turkish Bayraktar TB2 drones. The military authorities say the...
Tunisia: Journalist Zied El-Heni released from jail, gets six-month suspended sentence
Tunisian journalist El-Heni was released from prison on Wednesday, 10 January 2024, but he was given a six-month...
Four Mauritanian gold miners were killed last weekend near Gleibat El Foula ($)
JPMorgan de-lists Egypt from its Emerging Market Bond Index (S)
Mali army says it thwarted terror attack in Menaka ($)
Tunisia: Phosphate company signals recovery after a three-year decline (S)
Morocco-Mauritania relations: Tensions after killing by drone of Mauritanian civilians
The Moroccan media said the Mauritanian authorities have abruptly increase by 171% the customs duties applied to...
Algeria fires head of police, arrests 11 Oran Airport security officers
Farid Bencheikh, the head of gigantic police and security agency, the Director General of National Security (DGSN),...
Tunisia neutralizes human smugglers
The Tunisian police reported on January 7, 2024 the dismantling of an alleged human trafficking network in the Sfax...
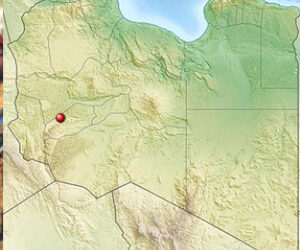
Libya: Protesters force closure of El Sharara oil field over local economics
The North Africa Journal - Protestors seeking social and economic development for the Fezzan region, located in the...
Sahel: Qatar helps dissipate diplomatic tensions between Mali and Algeria
The North Africa Journal - Qatar has demonstrated its diplomatic skills in the Middle East crisis but it has also been...
Sahel: Burkina Faso ratchets up war effort with new army units and taxes for voluntary militia
The North Africa Journal - The new year began in earnest in Burkina Faso, with fresh efforts from the government to...