The European Union’s revised migration framework, set to take effect in mid-2026, is already reshaping how migration...
Libya Bound
Libya: Turkey is Here to Stay, Abandons Exit Strategy
Turkey's parliament has approved a 24-month extension of its military deployment in Libya, running through early 2028....
Libya: Protesters Gather at UN Mission in Janzour Demanding Accelerated Elections, Warning of National Collapse
Dozens of demonstrators assembled outside the United Nations Support Mission in Libya (UNSMIL) headquarters in Janzour...
Libya’s latest official death toll exceeds 3,800
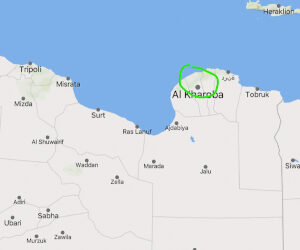
Nearly two weeks after a flash flood devastated the Libyan port city of Derna, the official death toll keeps rising,...
Podcast: And Now the Environment is Major Factor of Instability in North Africa
As we reach the end of the third quarter 2023, about to enter the tail-end of the year, it is difficult to see a...
Libya flood: As death toll exceeds 3,300, tens of thousands of people are displaced
Libya's flood disaster, which killed thousands in the city of Derna, also displaced more than 43,000 people, the...
Libya: Ancient Greco-Roman city of Cyrene faces risk of collapse
Floods that killed thousands in the Libyan city of Derna also inundated one of the country's premier ancient sites,...
Libya: Incompetent eastern authorities tighten control on media, block communications access
Communications were severed Tuesday to the flood-hit Libyan city of Derna and journalists were asked to leave, a day...
Libya: Entire families of Syrian migrants perished in flood
More than 100 Syrians, including entire families, died in flash flooding that killed thousands in Libya's eastern city...
Libya: ‘Worse than war’: Flood trauma haunts survivors
By Fulya Ozerkan: Grief etched into her face, 15-year-old Ibrar struggled to find the words to describe her pain at...
Libya: Phone and internet links severed in flood-hit Derna, day after protest
Telephone and internet links were severed Tuesday to Libya's flood-hit city of Derna, a day after hundreds protested...
Libya: Unrest in Derna
By Amanda Mouawad: Hundreds of protesters rallied in Libya's disaster-hit Derna on Monday, accusing the authorities of...
Libya: What is the storm that destroyed NE Libya? Meet Daniel
The flash flood that has killed thousands of people in Libya this week followed a "medicane", a rare but destructive...
Libya: The utter destruction of Derna
By Abdullah Doma: Rescuers sifted through mud and rubble Friday in their search for people missing from the...
Podcast: Libya’s Floods and Maghreb’s Leadership Deficit
Opinion by Arezki Daoud: The earthquake in #Morocco and the floods in #Libya should be an opportunity for "leaders" in...
Libya Floods: Latest Update
By Rim Taher: Flash flooding in east Libya caused by Storm Daniel tore through the coastal city of Derna, leaving...
Libya: Death toll surges to 2,300 in historical flood
At least 2,300 people were killed in Libya and thousands more were reported missing after catastrophic flash floods...
Libya: Major disaster unfolds, 10K people missing in storm-hit northeast
The death toll from freak floods in eastern Libya is expected to soar dramatically, with 10,000 people reported...
Libya: Freak floods hit northeastern, death toll could reach 2,000
At least 150 people were killed (North Africa Journal editors' note: count likely to reach or exceed 2,000) when freak...
Another tragedy in North Africa, at least 150 killed in Libyan floods
At least 150 people were killed in freak floods in eastern Libya as a result of storm Daniel which has swept the...
Libya PM fires Foreign Minister Najla El Mangoush after she met Israel’s counterpart
Libya's internationally recognised prime minister has sacked his top diplomat after she met her Israeli counterpart,...
French prosecutors allege ex President Sarkozy took money from Libya to fund election campaign
Former French president Nicolas Sarkozy will be tried in 2025 over allegations he took money from late Libyan dictator...
Libya says it captured IS militant behind three attacks in 2018
A leader of the Islamic State (IS) group who allegedly planned and sponsored three deadly attacks in the Libyan...
Libyan warlord Haftar invites the Russian military
Russian military officials including Moscow's deputy defence minister arrived in Libya on Tuesday after receiving an...
North African governments struggling with migrant crisis
Tunisia and Libya announced Thursday they had agreed to share responsibility for providing shelter for hundreds of...
Anti-migrant sentiment in North Africa turns into humanitarian disaster
In the unbearable midday heat, a Libyan patrol near the border with Tunisia comes across a black African man collapsed...
Libya strongman Haftar issues new threat over oil revenue
Libyan military strongman Khalifa Haftar, who backs the politically-split country's eastern administration, has...
Libya: Base hosting Wagner mercenaries supporting warlord Haftar attacked by drones
Drone strikes early Friday hit an airbase in Libya's east used by mercenaries of the Russian paramilitary group...
Libya: Rescue ship saves 86 migrants off Libyan coast
The migrant rescue ship Ocean Viking rescued 86 people off the coast of Libya on Tuesday as their vessel foundered...
Libya: Rival governments bicker over oil revenues, threaten to shut down oil operations
The east-based government, which does not recognise the authority of the Government of National Unity based in...
Libya arrests 50 foreign nationals over alleged illegal crypto mining operation in Zliten
Libyan authorities have dismantled a crypto mining operation in the country's west, the prosecution in Tripoli said...
Libya: Politically contested issues threaten normalization in Libya
UN envoy Abdoulaye Bathily (pictured here) said Monday that a deal between Libyan rival camps over long-delayed...
Libya: After wanting total destruction of his western rivals, warlord Haftar now calls for unified government
Libyan military strongman Khalifa Haftar called Friday for a unified government of technocrats to organise...
Libya: This is why Libya may not see peace for the time being
@arezkid #Libya: the son of notorious #Libyan #dictator #Gaddafi is in #prison for the wrong reason. #ebanon,...
Libya: UN calls for halt to Libya migrant detention, expulsion
The United Nations on Monday called on Libya to treat migrants and asylum seekers with dignity, highlighting concerns...
Libya: UN wants to secure elections in Libya, to put pressure on rival groups
The United Nations said Thursday it would work towards helping Libya's rival factions agree on contested points...
Libya: Can Libya’s rival politicians and their foreign backers finally agree on a stabilization plan?
Envoys of rival Libyan factions have agreed on the legal steps to hold much delayed presidential and legislative...
Libya: Two militia groups aligned with Tripoli government clash in Tripoli, spread terror
Gunshots rang out in Libya's capital on Monday following hours of fighting between two armed groups both aligned with...
Libya uses drones to attack smugglers in west of the country
Forces of Libya's Tripoli-based government launched drone strikes against suspected smuggling sites in the country's...
Libya: Ousting of Bashagha signals possible path to reconciliation
Arezki’s Opinion By Rim Taher: Oil-rich but war-scarred Libya has for years been ruled by two rival governments, but...
Libya: Fathi Bashagha, rival prime minister, ousted by eastern parliament
Related Content: The fleecing of Libya [listen as audio podcast] Also: How to Plunder a Nation: How the Ben Ali clan...
Libyan forces intervene to halt deadly clashes between rival militias
Libyan security forces said Sunday they had deployed in Zawiya after battles between armed groups in the western city...
Podcast: The Fleecing of Libya: Billions of Dollars Missing and Everyone is at Fault
In the post-Gaddafi era, corruption in Libya is endemic and metastasized. The culture of corruption is so ubiquitous...