By Arezki Daoud: This morning, I spent a little more money on gasoline at the pump in Miami, but I admit I expected to...
Morocco Detains Civic Activist Amid Online Speech Concerns
Authorities in Morocco have detained another young activist in what appears to be a developing pattern involving...
Tunisia: Arrest of Opposition Figure Olfa Hamdi Raises Concerns
A Tunisian civil liberties organization has publicly challenged the Tunisian authorities over the reported detention...
More from the Maghreb
Morocco’s Deficit Widens in Trade With Turkey
Economic ties between Turkey and Morocco are expanding at an unprecedented pace. Over the past two years, trade flows...
Tunisian Women’s Rights Group Warns Early Retirement Proposal Could Undermine Female Labor Participation
A new legislative proposal in Tunisia has triggered strong opposition from women’s rights advocates, who argue that...
French Interior Minister Renews Dialogue with Algeria
By Mondafrique: Initially scheduled for December 2025 and postponed a second time in January, the long-awaited visit...
Moroccan pharmacy unions push back against proposed ownership reforms
Morocco’s debate over whether to open pharmacy ownership to outside investors has sharpened after the Competition...
Morocco Allegations Reignite Spain’s Pegasus Debate
Spanish media commentary on the Pegasus episode involving Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez intensified this week (February...
Morocco: Employment Gains Concentrate in Urban Centers as Rural Areas Fall Behind
Recent employment data released by High Commission for Planning points to a marked acceleration in job creation in...
Southern Libya Boils Over: Three Haftar Soldiers Killed in Border Raid Near Niger
Three Libyan soldiers aligned with eastern warlord Khalifa Haftar were killed and several others captured in...
Tunisia Appeals Court Extends Rached Ghannouchi’s Prison Term by 20 Years
A court of appeals in Tunis has sharply increased the prison sentence handed to Rached Ghannouchi, the 84-year-old...
With Saif al-Islam Killed, Gaddafi Dynasty’s Political Ambitions All But Collapse
Saif al-Islam Gaddafi, one of the most prominent sons of Libya’s former ruler Muammar Gaddafi and long viewed as his...
Cyclone Harry’s Hidden Toll: NGOs Fear Up to 1,000 Migrants Lost at Sea
Humanitarian groups say the death toll from January’s Central Mediterranean storms may be far higher than official...
Morocco Reassures Public on King Mohammed VI’s Mechanical Lumbosciatica
Morocco’s Royal Palace has confirmed that King Mohammed VI is undergoing treatment for a mechanical lower‑back...
Agriculture: Drought‑Hit 2025 Season Leaves Morocco More Dependent on Cereal Imports, According to FAO
Morocco is heading into 2026 with a mixed outlook for its cereal sector, as favorable early-season conditions contrast...
French Prosecutors Target Ex-Algerian Minister in Corruption Case Tied to Sonatrach and the ICJ
French authorities have opened a financial crime investigation targeting Mohammed Bedjaoui, a former Algerian justice...
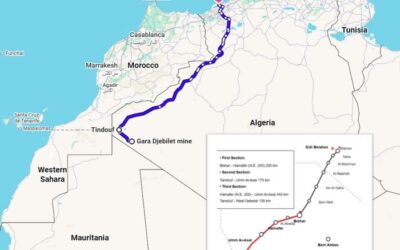
Algeria’s 2,000‑Kilometer Mining Corridor: Rail, Iron Ore, and the Road to the Mediterranean
Algeria has officially opened a new rail line that links the remote southwest to the Mediterranean, a move with...
French Law Eases Path to Nuclear Test Compensation for Algerian and Polynesian Victims
France’s National Assembly has unanimously approved a landmark reform that makes it easier for people harmed by its...
Africa Cup of Nations (AFCON 2025) in Morocco: Strong Hosting, Weak Crisis Management
Morocco delivered a technically strong Africa Cup of Nations in 2025. Stadiums were modern, logistics mostly worked,...
Climate: Severe Winter Rains Shut Down Schools in Northern Morocco This Week
Classes have been suspended across Ksar El Kébir from Monday, February 2 through Saturday, February 7, 2026, after...
UAE Regional Influence Under Strain Amid Sudan, Libya, Yemen, and Maghreb Frictions
Across several regions, the United Arab Emirates is facing visible diplomatic and political friction with key Arab...
Algeria Expands Core Infrastructure Investment Across Core Sectors
Algeria is continuing a broad, state-led investment drive focused on basic infrastructure, spanning roads, railways,...
Algerian Supporters Face Charges in Morocco
At least three Algerian nationals remain in custody in Morocco after traveling to the country to support their...
Morocco’s Lawyers Push Back Against Proposed Changes to Bar Governance
A standoff is emerging between Morocco’s legal profession and the Ministry of Justice over a draft law governing the...
Europe’s New Migration Rules Shift Pressure South to North Africa
The European Union’s revised migration framework, set to take effect in mid-2026, is already reshaping how migration...
Air Algérie Expands Long-Haul Capacity With Second A330-900neo
Algeria's airline carrier, Air Algérie, has taken delivery of its second Airbus A330-900neo as part of an ongoing...
Algeria: Supply Disruptions and Rising Food Prices Amid Transport Strike
A nationwide strike by freight transport operators that began last Thursday is increasingly affecting daily life in...
Irregular Migration to Spain Falls Sharply in 2025 With Decline in Atlantic Crossings
After reaching a historic high in 2024, irregular migration to Spain fell sharply in 2025. Official data show a...
How the US Intervention in Venezuela is Reviving Global South Fears of Power Politics
The US raid that captured Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro is resonating across Africa as part of a broader pattern...
Morocco: Financial Authorities Probe Distressed Property Transactions, Money Laundering Concerns Grow
Financial intelligence authorities in Morocco have placed parts of the real estate sector under heightened scrutiny...
Libya: Turkey is Here to Stay, Abandons Exit Strategy
Turkey's parliament has approved a 24-month extension of its military deployment in Libya, running through early 2028....
Tunisia: Leading Labor Union in Turmoil
The possible resignation of Noureddine Tabboubi, the general secretary of the UGTT (Tunisian General Labor Union), is...
Libya: Protesters Gather at UN Mission in Janzour Demanding Accelerated Elections, Warning of National Collapse
Dozens of demonstrators assembled outside the United Nations Support Mission in Libya (UNSMIL) headquarters in Janzour...
Algeria: Fuel Price Increase Triggers Brief Transport Disruption, Services Resume
Algeria entered 2026 with a moderate adjustment in domestic fuel prices, a move authorities say is necessary to secure...
Tunisian Equity Market Posts Record Gains in 2025
Despite the unsettling political realities of Tunisia, the country's equity market closed 2025 with one of its...
Rights Groups Warn of Widening Restrictions on Freedoms in Tunisia
The Tunisian League for Human Rights has issued a stark assessment of the country’s political and civil trajectory,...
Algeria: Rail, Water, and Transport Drive 2026 Infrastructure Spending
Algeria’s 2026 finance law, officially published in the government gazette on Wednesday and entered into force on...
U.S. Immigration Policy and the Changing Landscape of Africa-U.S. Travel
As the United States prepares to implement a new round of immigration and visa policy changes in 2026, the effects are...
Libya Enters 2026 With the Same Political Fragmentation and Sustain Bad Foreign Influence
As Libya enters 2026, the country remains caught in the same prolonged state of political suspension, where formal...
Tunis Appeals Court Upholds Prison Sentence Against Opposition Leader Abir Moussi
A Tunis appeals court has upheld a two-year prison sentence against opposition figure Abir Moussi, confirming an...
The UAE’s Growing Role in African Conflict Zones
Saudi–Emirati tensions over Yemen open a wider question: to what extent is the UAE using proxy actors, media leverage,...
North Africa Tests the Limits of Ride-Hailing as Uber Returns Under Tight Control
Morocco is once again testing the boundaries of app-based urban transport, reopening a politically sensitive debate...
Tunisia Shows Measured Economic Stabilization After Years of Strain
After several years of economic strain, Tunisia showed signs of gradual stabilization over the past 24 months. While...
Algeria’s External Rebalancing: Managing Strained Ties with France While Preserving Strategic Stability with the United States
Algeria's current foreign policy reflects a deliberate effort to recalibrate relations with France while maintaining...
Algerian Parliament Passes Law Criminalizing French Colonization
On December 24, 2025, Algeria's National People's Assembly unanimously approved legislation that designates French...
Environment: Algeria’s Race Against a Looming Water Collapse
Algeria is heading toward an acute water crisis, and the clock is ticking much faster than most policymakers admit....
Aviation: Ryanair Picks Rabat as New Low-Cost Aviation Hub
Ryanair, Europe’s largest low-cost airline by passenger volume, plans to establish a new operational base at...
Morocco: 2025 Crime Trends Show Declines in Violent Offenses and Improved Case Resolution
Morocco’s national police reported a stable overall crime picture in 2025, with one clear shift standing out: violent...
Tunisia: Supporters Rally in Tunis to Back the President and Reframe Tunisia’s Uprising
Thousands of supporters of Tunisia’s president gathered in central Tunis this week in a show of political support that...
Algeria to Introduce Digital Passport Renewal for Citizens Living Abroad
Algerian authorities are preparing to roll out an online passport renewal system for citizens living overseas, with...
Algeria: Inside the Draft Citizenship Revocation Law
Algeria’s lower house of parliament is reviewing a bill that would let the state strip some Algerians of their...
Business: As Relations With France Strain, Algeria Broadens Its Grain Suppliers
Algeria has been broadening its wheat supplier base in an effort recalibrate economic ties with France, long Algeria’s...
Algeria’s Parallel Currency Market Surges, Puts Pressure on the Dinar
The euro and the US dollar are trading at record levels on Algeria’s parallel currency market, widening the gap with...
Business: Chinese Logistics Platform Scouts Tunisia As Africa Gateway
Wuhan Yangluo Port Services, a Chinese state-linked entity active across trade, logistics, finance, and investment,...
Morocco: Urban Safety Concerns Grow Amid Deadly Floods and Building Collapse
Morocco has been experiencing a series of deadly urban disasters in recent days that have intensified scrutiny of...
Survey on French Muslims Reopens Debate on Religious Practice, Identity, and Interpretation
A recent survey conducted by the French polling institute IFOP has reignited debate about the religious attitudes of...
EU–Morocco Tomato Dispute Deepens Over Western Sahara Labeling
Allegations of unfair competition and labeling disputes are straining relations between Morocco and the European Union...
Algeria Raises Minimum Wage and Jobless Benefits for 2026
Algeria has approved increases to both the national minimum wage and unemployment benefits, starting in 2026,...
Tunisia’s Main Union Calls Nationwide Strike Amid Political Tensions
Tunisia’s main trade union federation has called for a nationwide general strike on January 21, 2026, to protest...
Algeria Rolls Out 5G Network with Six-Year Expansion Plan
Algeria has activated its 5G mobile network, with the formal launch occurring on December 3rd in Algiers. The...
Morocco’s Influencers Face Rising Legal Risks
Morocco’s courts are handling a growing number of cases involving high‑profile social media creators, signaling a...
Moroccan Streamer Ilyas El Maliki Arrested Again
Moroccan online streamer Ilyas El Maliki was detained on the evening of Monday, 25 November 2025 in the coastal city...
Morocco: Ex-Minister and Lawyer, Mohamed Ziane Still in Detention
Former Moroccan minister and lawyer Mohamed Ziane is currently detained on the basis of two distinct criminal cases,...
Washington Initiates Review Process for Possible Terrorism Designations of Muslim Brotherhood Branches
U.S. President Donald Trump announced on 23 November 2025 that his administration has initiated a formal review to...
US: Global Media Reacts to America’s Epstein Reckoning
The global media is following the Epstein scandal as a sign of political strain in Washington. The battle over the...
Libya: The Strange Case of Hannibal Gaddafi: From Exile to Detention to Release
Hannibal Gaddafi, the son of Libya’s former leader Muammar Gaddafi, was freed from a Lebanese jail in November 2025...
Algeria: 25 Executives Charged in Alleged Metals Fraud
A high-profile corruption trial involving Algeria’s state-owned metals conglomerate Imetal is set to begin on November...
Morocco: Two Years After the High Atlas Mountains’ Earthquake, Recovery Remains Uneven
In September 2023, a powerful earthquake struck Morocco’s High Atlas Mountains, killing nearly 3,000 people and...
Tunisia: Wage Dispute Triggers Widespread Bank Shutdowns in Tunisia
Thousands of employees in Tunisia’s banking, financial, and insurance sectors observed a remote strike on Monday and...
Algeria: Salima Melizi’s Case Highlights Algeria’s Cultural Tensions
The arrest and release of Salima Melizi, an Algerian writer and publisher known for her independent voice, has...
Morocco: Drought Pressure Threatens 2025-26 Farming Season
Morocco's 2025-26 agricultural season faces mounting difficulties due to sustained drought and diminishing water...
Tunisia: Economic Pressures Erode Household Purchasing Power
A recent Fitch Solutions report, “Consumption and Household Income in Tunisia,” published October 22, 2025, finds that...
Security Council Backs Morocco’s Plan for Western Sahara, Sets Out Negotiation Terms
The UN Security Council voted on October 31, 2025, to adopt a resolution regarding Western Sahara, which was drafted...
Algerian Lawmakers Consider Stripping Citizenship from Nationals Abroad
A plan resurfacing in Algeria’s parliament would allow authorities to strip citizenship from Algerians who commit acts...
Morocco’s New Election Law Sparks Free Speech Battle
Morocco’s government has just approved a controversial change to its election law—setting out steep new penalties for...
Tunisia: Pollution Uprising in Gabès Turning Into Sustained Protest Movement
MondAfrique: Gabès' fight against pollution has reached historic levels, turning into a sustained protest movement...
Libya: NOC Expands Exploration as Libya Targets 1.6 Million Barrels by 2026
Libya is pressing ahead with a broad-based energy revival that combines renewed foreign exploration, fresh domestic...
Morocco: Forces Drive Morocco’s 2026 Budget: Security Recruitment Leads Job Creation Push
Morocco’s 2026 draft Finance Bill sets out one of the country’s most ambitious recruitment plans in years, creating...
Algeria Widens Anti-Corruption Crackdown, From Trade Ministry to Waste Agency
Algeria’s judiciary has recently unveiled two major corruption cases, highlighting widespread misconduct across key...
Morocco Strengthens Global Standing with Record Tourism Growth
Morocco’s tourism sector continues its post-pandemic climb, welcoming 15 million visitors between January and...
Algeria Pushes for Ambitious Cashless Economy by 2028
Algeria says it will transition to a completely cashless economy by 2028, according to an official plan led by the...
Morocco’s Youth Protests Regain Momentum, Calls for Reform Ahead of 2025 Africa Cup
Morocco’s youth-led protest movement, GenZ212, returned to the streets on Saturday, October 18, after a short pause,...
Tunisia: Protests in Gabès Over Pollution and Repression
Over the past week, Gabès, in Tunisia, has seen a dramatic escalation in social unrest centered on anti-pollution...
Algeria: Diphtheria Death Sparks Outbreak Fears in Skikda
The province of Skikda is experiencing anxiety after the announcement on Thursday of a death caused by diphtheria....
Washington Returns to Libya’s Frontlines in Bid to Counter Russia and Reunify Militias
U.S. Africa Command (AFRICOM) has announced that Libya, long divided between rival political and military factions,...
France Signals a Thaw in Its Rift with Algeria
France has signaled a possible thaw in its strained relationship with Algeria after several tense months marked by...
Algeria and Tunisia Expand Military Cooperation Amid Regional Security Tensions
In a move reflecting the deepening security alignment between Algeria and Tunisia, the two neighbors signed a new...
Morocco: GenZ212 Makes Tactical Pause in the Fight for Reforms
The GenZ212 protest movement in Morocco, which emerged following the deaths of eight women in an Agadir hospital, has...
Algeria: Retailleau’s Departure Opens Door to a Possible Reset in France–Algeria Ties
The departure of France’s interior minister Bruno Retailleau marks a substantial moment against the backdrop of...
Sonatrach Signs $5.4 Billion Exploration Deal With Saudi Firm Midad Energy
Algeria’s state-owned energy company Sonatrach has signed a $5.4 billion exploration and production agreement with...
Libya’s Path to Stability: Still Blocked by Fragmentation and Armed Rivalries
Libya closes 2025 still caught in a web of armed rivalries, political fragmentation, and recurring violence that...
Depression: Tunisia, Morocco, and Libya Among Africa’s Highest Prevalence Countries
North Africa is facing an acute mental health challenge, with three of its countries—Tunisia, Morocco, and...
Algeria’s 2026 Budget Plan: Spending Rises with Emphasis on Salaries, Subsidies, and Investment
Algeria’s draft finance law for 2026 marks a significant increase in public expenditure, with total spending projected...
Algeria Plans Major Military Budget Increase for 2026
Algeria is set to approve a substantial increase in defense spending for 2026, marking the largest allocation ever...
Tunisian SMEs Warn of Economic Paralysis Over 20% Bank Guarantee Rule
A new rule requiring small and medium-sized Tunisian businesses to provide a 20% bank guarantee for service contracts...
Morocco Boosts Russian Oil Imports Despite Sanctions
Morocco increased its imports of Russian petroleum products in August, defying ongoing Western sanctions on Russian...
Tunisia: Diaspora Funds Provide Lifeline for Tunisia’s Economy
Remittances from Tunisians living abroad reached 6.5 billion dinars (approximately $2.05 billion USD) by the end of...
Northwest Africa’s Fishing Crisis Intensifies
In Nouadhibou, Mauritania’s bustling fishing hub, the docks don’t hum the way they once did. Factories that once...
Why Morocco’s Protests Aren’t Just About Youth: The Fight for Dignity and Justice
Transcript Morocco is once again at the center of deep civil unrest, drawing international attention—not least from...
Morocco: Youth-Led Protests Spur Police Crackdown Across Moroccan Cities
A wave of youth-driven demonstrations swept through Morocco over the past several nights, with rallies unfolding in at...
Algeria: Former Labor Minister Receives Prison Sentence for Role in Public Funds Misuse
Algerian authorities continue to hand down verdicts stemming from investigations into corruption scandals dating back...
Algeria: Air Algérie Adds Over 100 Weekly Domestic Flights in Network Expansion
Algerian state airline carrier Air Algérie is expanding its domestic flight network, following its previous...
The Brutal Downfall of Former French President Nicolas Sarkozy
Former French President Nicolas Sarkozy is now facing the prospect of prison, after being sentenced on September 25,...